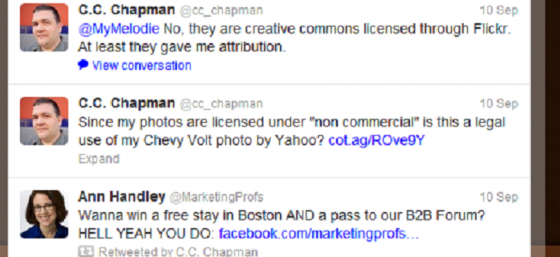
I saw the following tweet the other day by author C.C. Chapman: “Since my photos are licensed under “non-commercial” is this a legal use of my Chevy Volt photo by Yahoo?” The question was followed by a link to an article on Yahoo Auto about GM’s report regarding whether Chevy Volts are being sold at a loss. The photo accompanying the article is C.C. Chapman’s photo of a Chevy Volt that he published on Flickr with a Creative Commons license.
![]() This license requires anyone who uses the image to give C.C. Chapman the attribution, only use it for non-commercial use, and not alter the photo in any way. If the image appeared on Chevrolet’s blog, there would be a strong argument that Chevy uses its blog as a marketing tactic to get people to buy its vehicles; therefore every image on the blog is being used for a commercial use. In that case, the use of the image would have violated the license and C.C. Chapman’s copyright.
This license requires anyone who uses the image to give C.C. Chapman the attribution, only use it for non-commercial use, and not alter the photo in any way. If the image appeared on Chevrolet’s blog, there would be a strong argument that Chevy uses its blog as a marketing tactic to get people to buy its vehicles; therefore every image on the blog is being used for a commercial use. In that case, the use of the image would have violated the license and C.C. Chapman’s copyright.
However, Yahoo published the article. Yahoo isn’t trying to sell cars. It makes money by selling ads and it may charge advertisers based on the number of hits a page gets. C.C. Chapman could make an argument that Yahoo’s use of his photo had a commercial goal; but Yahoo could fire back that it was reporting the news so its use of C.C. Chapman’s photo was protected by fair use. Yahoo could show that it has a history of news reporting and that its articles are accepted as news, not a marketing ploy.
But let’s say this photo appeared on a commercial website in violation of the Creative Commons license. That’s copyright infringement. What could C.C. Chapman do about it?
- Do nothing and be happy about the exposure.
- Get the photo removed by sending a DMCA takedown notice.
- Send the company a cease and desist letter.
- Send a bill with a licensing agreement and a letter that says the publisher has committed himself to paying a licensing fee since he already used the photo.
- Sue for copyright infringement.
A lot of people would be happy about the exposure and may opt to do nothing. The downside of doing this is someone else could use your work and make a valid argument that your inaction set a precedent that others could use their work for commercial purposes. You may want to send a letter that offers to license the photo in exchange for the exposure and states if the company doesn’t license it then they have to remove it. That way, you will still get your exposure but you still exert your copyright rights in your work.
If you have questions about how to protect your intellectual property rights, contact an intellectual property attorney (like me) in your community.
Feel free to connect with me via Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn, or you can email me.
Please visit my homepage for more information about Carter Law Firm.
Lights Camera Lawsuit
There’s always a need for quality legal information for photographers. That’s why I created an online course called Lights Camera Lawsuit: The Legal Side of Professional Photography to address photographers’ most important questions. I want you to feel secure in your business, confident in the way you operate day-to-day, knowing that you’ve set yourself up to get paid what your worth without incident.
At $497, the course contains nearly six hours of legal information you can immediately apply to your business. That’s less than what I charge for two hours of legal work for clients!
Please subscribe for more information and to make sure you don’t miss out on any special offers or discounts.